Share this post
Tariffs, import duty and tax: what’s the difference?
Tariffs, import duty and tax are often mixed up with one another.
Much of it overlaps and is used interchangeably which can make it all quite confusing. However, it’s really important to get the distinctions right, especially when it comes to your trade obligations and agreements in international shipping.
Tariff, import duty and tax: a quick look
A tariff dictates the rate of duty.
An import (also known as a customs duty) is a fee charged on almost every cross-border shipment of products, and varies based on the Harmonized Tariff Schedule (HTS) codes and their destination. You can look up the item’s HTS tariff code on the HTS database.
Alcohol is based on litres and/or alcoholic strength (proof). While other HTS codes are based on the value of the products, number of pieces or kilo weight.
Alongside common tariff duty, additional excise duty is applicable on alcohol, hydrocarbon oils and tobacco.
Tariffs are usually imposed to regulate the trade of foreign products and depend on country of origin.
Value-added tax (VAT) is a type of consumption tax separate from a customs duty, of special importance in the European Union (EU). It is applied to imported and domestic products and services.
Australia and New Zealand have Goods and Services tax (GST), which is equivalent to VAT.
Who pays for a custom duty and tax, varies according to the Incoterm®.
What are taxes?
A tax is a source of government revenue.
It is compulsory and applies to all products. In international shipping, taxes are added to almost all products.
These taxes are obligatory by law. Import/consumption taxes are the fees applied to products entering a country, usually paid by the importer to customs.
They’re a way in which governments can protect local products by restricting foreign products from flooding and dominating their market. By taxing a foreign product, it becomes less appealing to purchase, since the price of it goes up by comparison to say a home-grown item.
The idea, is that by buying your own country's products, you are contributing to your local economy. Any time you import a product into a country, and that item is taxable and above a minimum value, you’ll pay a duty or tariff fee.
What is a custom duty?
Duties are indirect taxes, similar to consumption tax.
They’re referred to as indirect because the seller or producer who initially pays the duty will try to pass the charge on to the end consumer, incorporating it into the purchasing price of the product. In other words, the end consumer isn’t directly responsible for paying the fee to the government, but they end up covering that tax cost anyway by paying more for the product.
A custom duty is set during international trade negotiations between countries, and can vary wildly from 0% up to 40% (according to worldbank.org) of the import value of the product, depending entirely on the destination country.
An import duty of a certain product may only be 5% in one country, but 30% in another country - even though it’s the exact same product. Import duties are only charged on products crossing international borders.
An excise duty is chargeable in addition to any customs duty which may be due on the products. Excise is applicable to Fuels (Hydrocarbon Oils & biofuels), alcohol and tobacco products.
Importing countries calculate and control these costs, which are generally payable on products regardless of origin, once released for consumption.
An excise duty is a tax that’s imposed on specifically classed ‘excise goods’, including:
Alcohol
Fuel
Tobacco
Its purpose is to reduce the consumption of certain products that may have a harmful effect on human health or the environment. This excise tax is charged for locally produced products as well as on imported products.
Again, this cost is incorporated in the buying price. Because an excise duty is not exclusively for imported products, it’s not technically always an import tax.
What are tariffs?
In contrast to a custom duty, tariffs are import taxes that are only charged on products arriving from another country.
They can be implemented relatively quickly, and recently we’ve seen them used to penalise the trade of goods from a country, e.g. China’s tariff on Australian wines and the US and EU Boeing issues.
Tariffs, duties and taxes: How to calculate the cost of an import duty or tariff on my products?
To calculate how much the duty or tariff on your products are, check your product’s 7-10 digit HTS code and then look for your product on the HTS database here.
Alternatively, ask your freight forwarder who can find this code and do this step for you. Incoterms® are vital to determining whether the seller or buyer takes responsibility for paying the customs duties in any shipment.
We’ve written a useful summary of the current Incoterms® here.
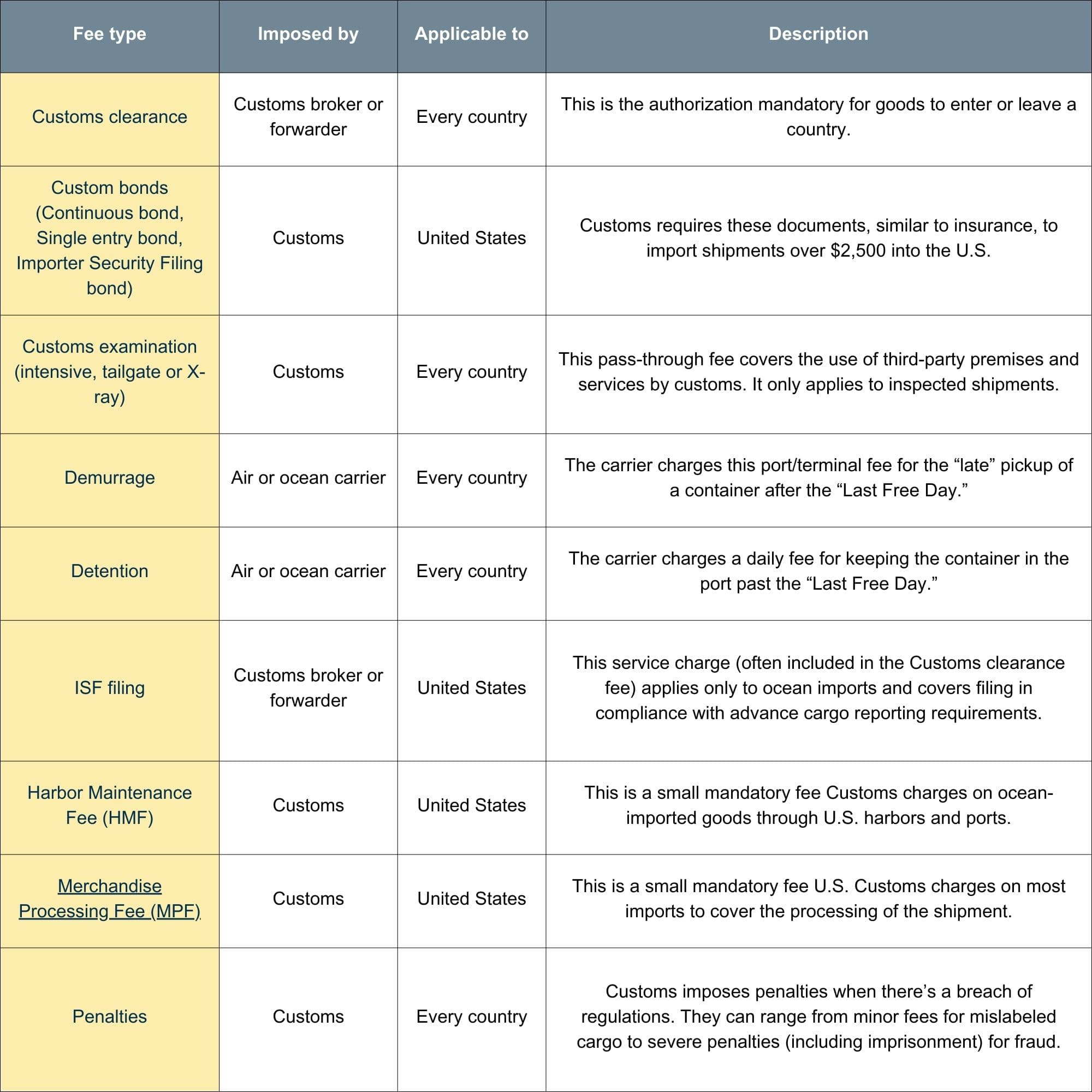
Custom duty charges
Customs duty charges vary depending on the country of origin and product type.
Here is a breakdown of charges explaining who’s liable to pay and why:
Let Hillebrand Gori help you navigate the complex customs landscape
We're experts in global customs regulations and provide custom clearance services worldwide.
Regardless of the origin or destination of your cargo, we'll make sure it gets there safely while adhering to the legal, legislative and regulatory requirements of each country.
If you need a quote or still confused by the terms tariff, import duty or tax is, contact us, we’re here to help!
Published 12th May 2023, updated 27th February 2024
Yes, import duties are taxes imposed on products entering a country. The type of products and their value usually determine the rate of duty.
Yes, there may be exemptions or reduced rates for duties and taxes depending on the country of import and the type of products. For example, in the United States, there’s a duty exemption for products with a total value below $800 (de minimis value). But the de minimis rule doesn’t apply to beer, wine and other fermented beverages.
The receiver of the goods is usually responsible for paying duties and taxes because customs levy them in the destination country. However, the sender can also pay these fees on behalf of the receiver and collect payment from them later.
Work with a logistics provider, like Hillebrand Gori, who can help navigate the complex rules and regulations surrounding international beverage trade and ensure compliance. Another strategy is to use free trade agreements, which can lower, defer or eliminate duty rates for certain products traded between specific countries.
How can we help your business grow?





